Today, where information flows freely and educational models continue to evolve, the role of parents in assisting children with their homework has led to a wealth of opinions and perspectives.
The argument here is whether parents should actively engage in the academic pursuits of children, or take a more hands-off approach.
Furthermore, does parental involvement serve as a valuable support system or a hindrance to academic excellence?
What is Homework?
Homework refers to assigned tasks or assignments that children are expected to complete outside of their regular classroom hours. It is an integral part of a student’s academic journey.
It reinforces and extends what students have learned in the classroom. This provides them with additional practice, and promotes independent learning. Homework also helps students develop crucial skills such as time management and independent problem-solving.
The design of homework can take various forms, including written exercises, reading assignments, research projects, problem-solving exercises, and more.
The amount and type of homework assigned can vary widely depending on the grade level, subject, and educational philosophy of the school or teacher. Some schools have policies that aim to strike a balance between the benefits of homework and the potential drawbacks, such as excessive stress and reduced free time for students.
The Benefits of Parental Involvement
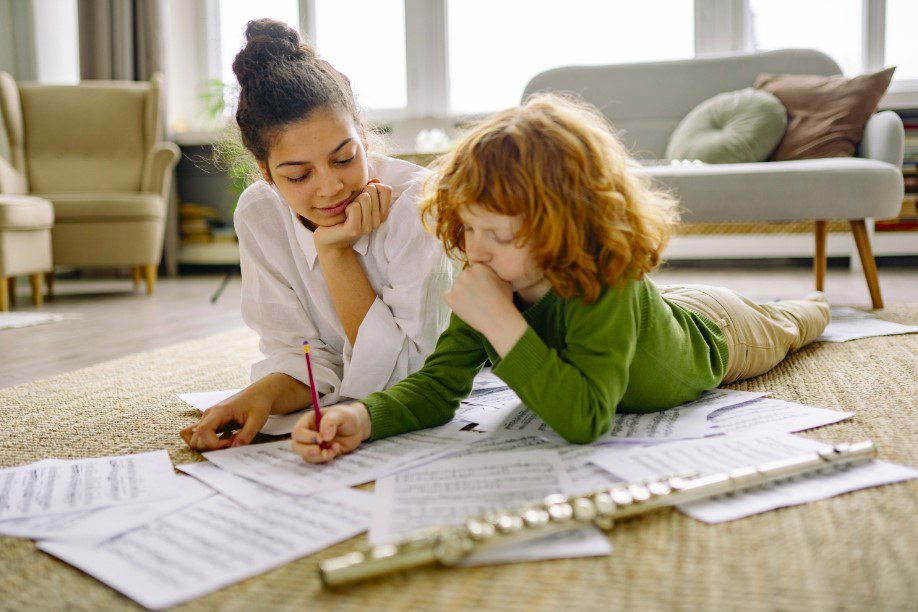

Parents are their child’s first teachers, and their involvement in the learning process is paramount. It sets the foundation for children’s educational journey. It is therefore important to recognize the significant role they play in the education of children.
1. Enhanced Learning Experience
When parents actively engage in their child’s homework, they enrich the whole learning experience. Parents can offer explanations, clarify doubts, and provide real-life examples that reinforce classroom lessons. This personalized approach can significantly improve a child’s comprehension and retention of knowledge.
2. Improved Motivation and Accountability
Children find it easier to stay motivated and accountable when they know their parents are part of their education. The presence of a supportive figure can encourage them to complete their homework diligently, knowing that their efforts are acknowledged and appreciated.
3. Identifying Learning Difficulties
Regular involvement can help parents identify any learning difficulties or areas where their child may need additional help, leading to early intervention if necessary.
4. Strengthened Parent-Child Bond
Homework can serve as a bonding opportunity for parents and children. Working together on assignments not only strengthens their relationship but also creates a positive attitude toward learning. It fosters open communication and allows parents to understand their child’s academic strengths and weaknesses better.
5. Time Management Skills
Parents can help children develop effective time management skills by setting aside dedicated homework time and teaching them how to prioritize tasks.
6. Self-Discipline
Parental involvement teaches children self-discipline, in that they learn to focus on and complete their homework before engaging in leisure activities.
7. Better Social Skills and Classroom Behavior
Students whose parents are involved in their homework are more likely to have good social skills and classroom behavior. This is likely because parents can help their children develop important communication and problem-solving skills, and they can also provide positive reinforcement for good behavior.
The Drawbacks of Parental Involvement in Homework for Children
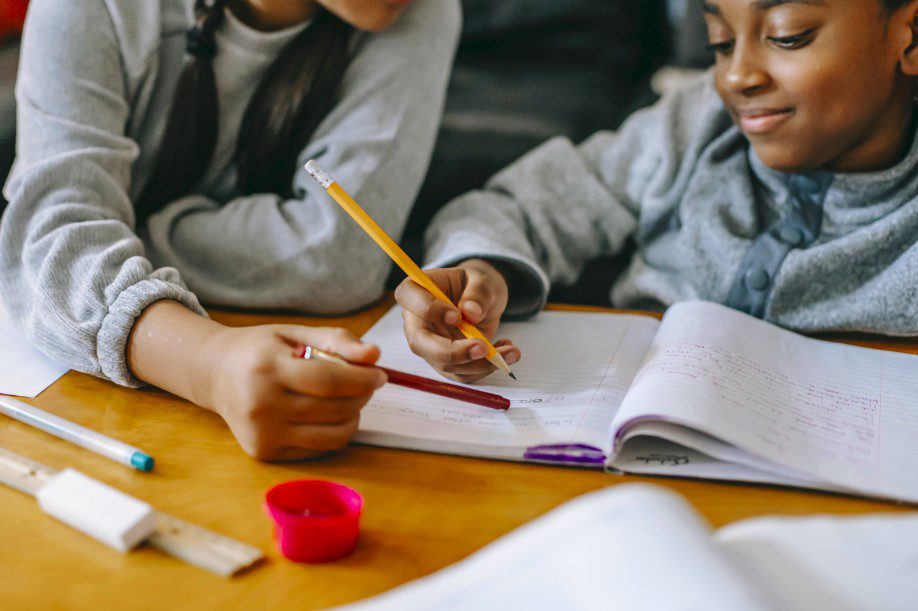

While parental involvement in homework has its merits, it’s essential to be aware of potential pitfalls that may arise when parents become overly involved.
1. Dependence
One potential drawback is the risk of creating dependence. If children become reliant on their parents for answers and solutions, they may struggle to develop essential problem-solving skills and self-reliance, which are vital for their long-term academic success.
They might become passive learners, expecting solutions to be handed to them rather than actively engaging with the material. This can hinder their ability to think critically and solve problems independently.
2. Stress
In some cases, parental involvement can inadvertently lead to increased stress for both parents and children. Homework sessions may become tense if parents have differing opinions on how tasks should be completed. This stress can have a detrimental impact on the child’s overall well-being.
Also true, parents who are unfamiliar with the subject matter or educational methods may experience frustration and stress when attempting to assist their children. This can create a tense atmosphere at home.
3. Inaccurate or Misleading Information
Well-intentioned but uninformed parents may inadvertently provide incorrect information or guidance to their children, potentially leading to misunderstandings or mistakes in the child’s work.
4. Reduced Creativity and Problem-Solving
When parents take over the homework process, children may miss out on the opportunity to develop their creativity and critical thinking skills. Homework should be a chance for children to explore and learn on their own, and excessive parental involvement can stifle this process.
5. Potential for Plagiarism
If parents are heavily involved in their child’s homework, there is a risk of unintentional plagiarism. Children may rely too heavily on their parents’ input, which can lead to a lack of originality in their work.
Striking the Right Balance
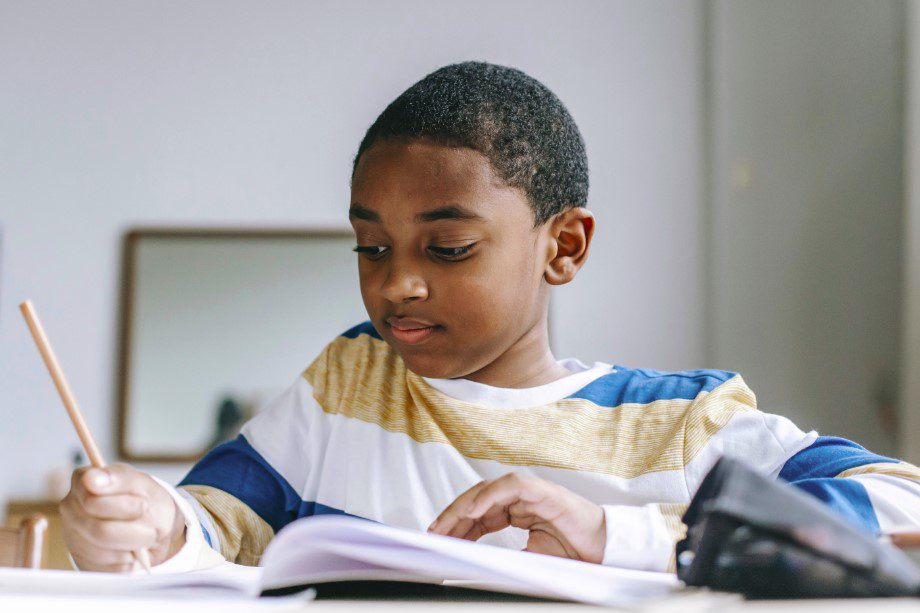

So, where does the balance lie? Is parental involvement in homework helpful or harmful?
The answer is a delicate one — it is both. Striking the right balance is key to reaping the benefits while avoiding the drawbacks mentioned above.
Here are some strategies for achieving this equilibrium:
1. Encourage Questions Instead of Answers
Parents should encourage their children to mostly ask questions and seek clarification when they encounter challenges with their homework. By fostering a questioning mindset, children learn to discover answers on their own.
Instead of giving answers outright, ask probing questions to help your child think critically about the problem.
For example, you can ask,
“What do you think the next step is?” or
“Can you break the problem down into smaller parts?“
2. Provide Resources
Make sure that resources such as textbooks, online references, or tutoring services are readily available to assist children when they need help. Have math tools such as rulers, protractors, and calculators available for math assignments.
Provide science supplies like magnifying glasses or a small microscope for science projects. Keep a stash of art supplies like colored pencils, markers, and craft materials for creative projects.
Encourage them to utilize these resources before seeking answers from parents.
In addition:
Provide Reference Materials: Stock the home with age-appropriate reference materials like dictionaries, encyclopedias, and relevant textbooks to aid in research and understanding.
Access to Technology: If possible, provide access to a computer or tablet for online research, typing assignments, and accessing educational websites.
Internet Safety: Ensure that there are parental controls and safety measures in place when your child uses the internet for homework.
Encourage Reading: Keep a variety of age-appropriate reading materials at home to promote a love for reading and improve literacy skills.
Encourage Curiosity: Foster your child’s natural curiosity by engaging in discussions about various topics and encouraging them to ask questions.
Online Educational Resources: Explore reputable educational websites and online learning platforms that align with your child’s curriculum.
4. Foster Independence
Promote independence by encouraging children to think critically and find solutions to problems on their own. When they encounter challenges, guide them towards resources or strategies that can help, rather than providing immediate answers.
5. Communicate with Teachers
Maintain open lines of communication with teachers to understand the curriculum and expectations. Teachers can provide valuable insights into how parents can best support their child’s learning journey without overstepping boundaries.
6. Be Supportive, Not Overbearing
Above all, parents should be supportive and nurturing in their approach. Offer praise for effort and improvement, and be patient when your child faces academic challenges. The goal is to create a positive and encouraging learning environment.
The Final Verdict
In conclusion, parental involvement in homework can be both helpful and harmful, depending on the extent and nature of the involvement. When done correctly, it can help children learn better and develop good study habits.
However, when done incorrectly, parental involvement can actually hinder students’ learning and make them more stressed.
Striking the right balance is essential to ensure that children receive the support they need while still developing vital skills for independent learning. Ultimately, the key is to foster a positive and nurturing environment that encourages growth and self-discovery.




Leave a Reply