Lifestyle ‘medicine‘ is an emerging field focused on using healthy habits to prevent, treat, and sometimes reverse chronic diseases. It is all about using evidence-based lifestyle approaches that promote the modification of daily habits and behaviors for better health.
Lifestyle medicine practitioners work collaboratively with health conscious individuals and patients to create tailored plans that can achieve sustainable health improvements and prevent the onset or progression of chronic diseases.
At the end of the day, this modification of lifestyle also reduces the endemic reliance humans have on pharmaceuticals.
The approach to this kind of lifestyle is grounded in seven key pillars:
1. Whole-food, Plant-based Diet
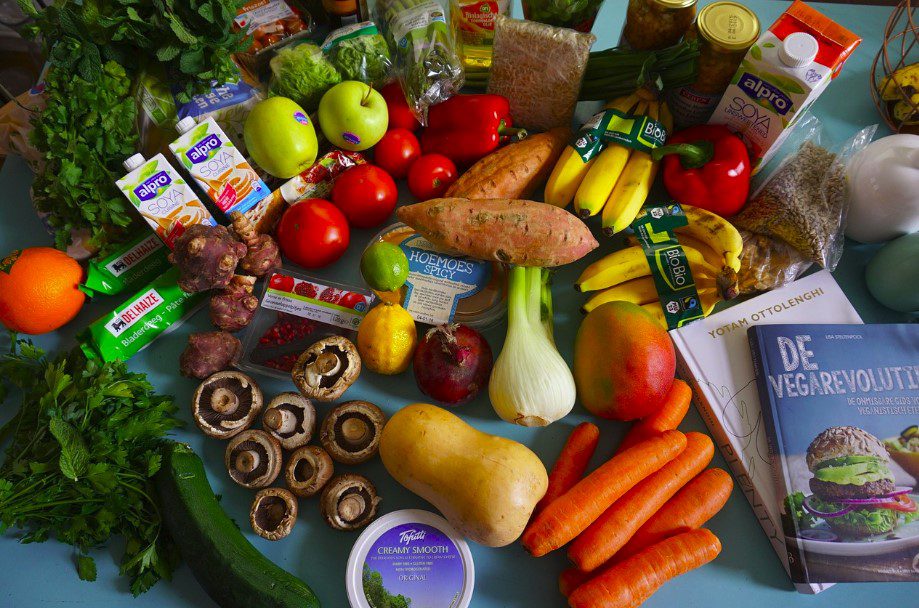

A whole-food, plant-predominant diet or plant-forward eating patterns, is central to lifestyle medicine and focuses on consuming foods in their most natural form. This means minimizing processed foods, and emphasizing plant-based ingredients.
Components of a Good Diet:
- Fruits and Vegetables: These should make up a significant portion of the diet. They are rich in vitamins, minerals, antioxidants, and dietary fiber, which are crucial for overall health.
- Legumes: Beans, lentils, and peas are excellent sources of protein, fiber, and other essential nutrients.
- Whole Grains: Foods like brown rice, quinoa, oats, and whole wheat products are preferred over refined grains.
- Nuts and Seeds: These provide healthy fats, protein, and various vitamins and minerals.
- Minimally Processed Foods: The focus is on foods that are as close to their natural state as possible. This means avoiding highly processed items that often contain added sugars, unhealthy fats, and sodium.
Benefits:
- Reduced Risk of Chronic Diseases: A diet rich in whole, plant-based foods has been shown to reduce the risk of many chronic diseases. These include heart disease, diabetes, and certain cancers (American College of Lifestyle Medicine).
- Nutrient Density: Whole plant foods are nutrient-dense, meaning they provide a high amount of nutrients and fiber for relatively few calories. This helps in maintaining a healthy weight and overall nutritional status.
- Improved Digestive Health: The high fiber content in fruits, vegetables, legumes, and whole grains aids in digestion and can help prevent constipation and other digestive issues.
- Blood Sugar Regulation: Consuming vegetables before other food groups can aid in regulating blood sugar levels. Research on diabetes suggests that starting a meal with vegetables can result in lower post-meal glucose levels compared to eating vegetables at the end of the meal. The dietary fiber in vegetables slows the absorption of sugars and starches, leading to more stable blood glucose levels.
- Better Weight Management: Plant-predominant diets are generally lower in calories and higher in fiber, which can help with weight loss and maintenance (Study Finds).
- Environmental Benefits: Plant-based diets have a lower environmental impact compared to diets high in animal products, contributing to sustainability efforts.
Practical Tips:
- Start Small: Gradually increase the number of plant-based meals you eat each week.
- Explore New Recipes: Try new plant-based recipes to keep meals interesting.
- Read Labels: When buying packaged foods, look for items with minimal ingredients and no added sugars or unhealthy fats.
- Plan Ahead: Meal planning can help ensure you have healthy, whole-food options available throughout the week.
2. Physical Activity
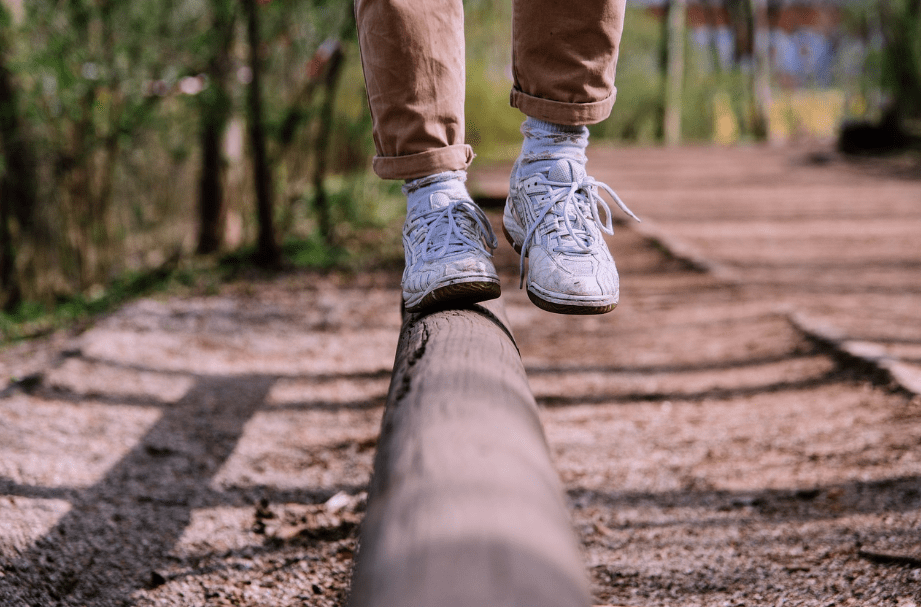

Physical activity offers numerous health benefits and plays a significant role in the prevention, treatment, and reversal of chronic diseases.
Key Aspects of Physical Activity:
- Types of Physical Activity:
- Aerobic Exercise: Activities like walking, running, cycling, and swimming that increase heart rate and improve cardiovascular health.
- Strength Training: Exercises such as weight lifting, resistance band exercises, and body-weight exercises that build muscle and bone strength.
- Flexibility and Balance: Activities like yoga, stretching, and tai chi that improve flexibility and balance, reducing the risk of falls and injuries.
- Recommended Guidelines:
- Adults: At least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity or 75 minutes of high-intensity aerobic activity per week, combined with muscle-strengthening activities on two or more days a week.
- Children and Adolescents: At least 60 minutes of physical activity daily, including aerobic, muscle-strengthening, and bone-strengthening activities.
Benefits:
- Cardiovascular Health: Regular physical activity strengthens the heart, lowers blood pressure, and improves cholesterol levels, reducing the risk of heart disease and stroke.
- Weight Management: Exercise helps maintain a healthy weight by burning calories and building muscle, which boosts metabolism.
- Diabetes Management: Physical activity improves insulin sensitivity and helps control blood sugar levels, which is crucial for managing and preventing type 2 diabetes.
- Mental Health: Exercise reduces symptoms of depression and anxiety, enhances mood, and improves cognitive function. It also helps manage stress by releasing endorphins and providing a healthy outlet for tension.
- Bone and Muscle Strength: Weight-bearing and resistance exercises increase bone density and muscle strength, reducing the risk of osteoporosis and sarcopenia (age-related muscle loss).
- Longevity: Regular physical activity is associated with a longer lifespan and a lower risk of premature death from various causes.
Practical Tips:
- Start Slowly: If you’re new to exercise, begin with low-intensity activities and gradually increase the intensity and duration.
- Find Activities You Enjoy: Choose exercises that you find enjoyable and that fit into your lifestyle, making it more likely that you’ll stick with them.
- Incorporate Physical Activity into Daily Routine: Take the stairs instead of the elevator, walk or bike to work, or engage in active hobbies like gardening.
- Set Realistic Goals: Set achievable fitness goals and track your progress to stay motivated.
- Stay Consistent: Consistency is key. Make physical activity a regular part of your daily routine.
3. Restorative Sleep
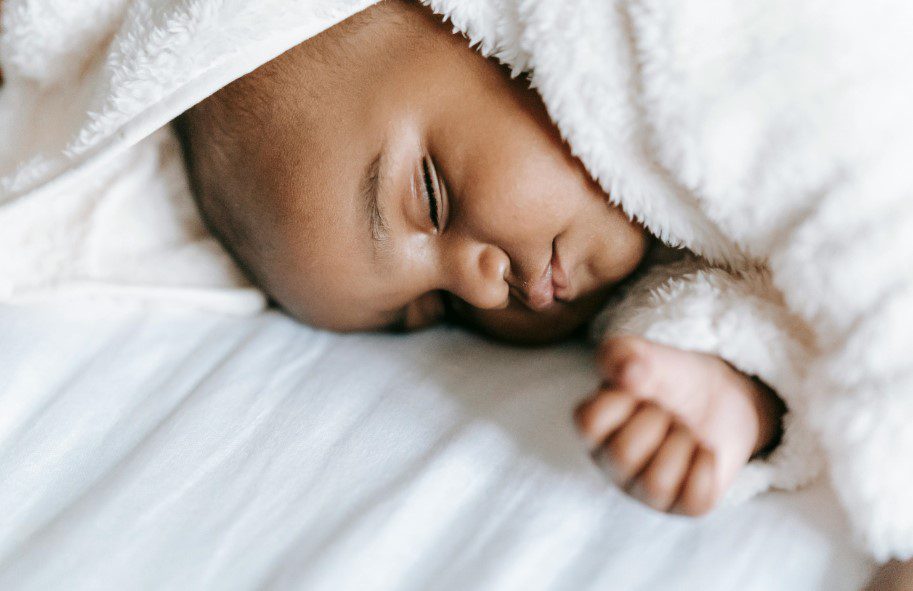

Restorative sleep is essential for overall health and well-being. Quality sleep supports various bodily functions and can significantly impact physical, mental, and emotional health.
Key Aspects of Good Quality Sleep:
- Sleep Duration:
- Adults: 7-9 hours of sleep per night is recommended.
- Teenagers: 8-10 hours per night.
- Children: 9-12 hours per night for school-aged children and even more for younger kids.
- Sleep Quality:
- Consistency: Going to bed and waking up at the same time every day.
- Sleep Environment: A quiet, dark, and cool room can improve sleep quality.
- Sleep Hygiene: Practices like avoiding screens before bed, limiting caffeine and heavy meals in the evening, and engaging in relaxing activities before sleep can enhance sleep quality.
Benefits:
- Cognitive Function: Good sleep improves attention, memory, and problem-solving skills. It also reduces the risk of cognitive decline and neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer’s.
- Emotional Well-being: Adequate sleep helps regulate emotions and reduces the risk of mood disorders such as depression and anxiety.
- Physical Health: Quality sleep supports immune function, reducing the risk of infections and chronic diseases such as heart disease, diabetes, and hypertension. It also promotes healthy growth and repair of body tissues.
- Metabolic Health: Proper sleep helps regulate appetite and metabolism, reducing the risk of obesity and associated conditions like type 2 diabetes.
- Performance and Safety: Sufficient sleep enhances performance and reduces the risk of accidents and injuries, particularly in activities that require attention and coordination.
Practical Tips:
- Establish a Routine: Go to bed and wake up at the same time every day, even on weekends.
- Create a Sleep-friendly Environment: Make your bedroom dark, quiet, and cool. Consider using blackout curtains, earplugs, or white noise machines if necessary.
- Limit Screen Time: Avoid screens (phones, tablets, computers) at least an hour before bedtime as the blue light can interfere with your sleep cycle.
- Be Mindful of Food and Drink: Avoid heavy meals, caffeine, and alcohol close to bedtime as they can disrupt sleep.
- Incorporate Relaxation Techniques: Engage in calming activities before bed, such as reading, taking a warm bath, or practicing meditation or deep breathing exercises.
- Physical Activity: Regular exercise can promote better sleep, but try to avoid vigorous activity close to bedtime.
4. Stress Management
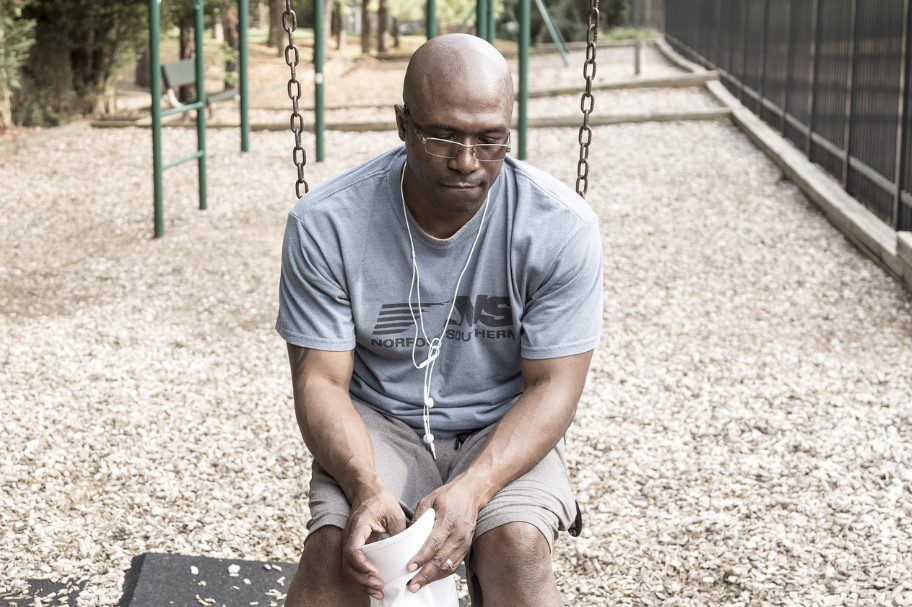

Stress management is a crucial component of lifestyle medicine, focusing on techniques and practices to reduce chronic stress, which can have profound effects on both physical and mental health.
Key Aspects of Stress Management:
- Mindfulness and Meditation:
- Mindfulness: Practices like mindfulness and meditation involve focusing on the present moment and accepting it without judgment. This can help reduce stress and improve overall well-being.
- Meditation: Various forms of meditation, including guided meditation, transcendental meditation, and loving-kindness meditation, can help reduce stress and promote relaxation
- Physical Activity:
- Regular exercise helps manage stress by releasing endorphins, which are natural mood lifters. Activities like yoga, tai chi, and even walking can be particularly effective.
- Healthy Sleep:
- Ensuring adequate, restorative sleep can significantly reduce stress levels. Good sleep hygiene practices are essential for managing stress effectively (Study Finds).
- Social Connections:
- Maintaining strong, supportive relationships with friends and family can provide emotional support and help buffer against stress. Engaging in social activities and seeking support when needed are important strategies.
- Relaxation Techniques:
- Techniques such as deep breathing exercises, progressive muscle relaxation, and guided imagery can help activate the body’s relaxation response and reduce stress.
- Time Management:
- Effective time management skills can help reduce stress by prioritizing tasks, setting realistic goals, and breaking projects into manageable steps (Study Finds).
Benefits:
- Mental Health: Effective stress management can reduce the risk of anxiety, depression, and other mental health disorders. It also enhances mood and overall mental well-being.
- Physical Health: Chronic stress is linked to various health problems, including heart disease, hypertension, diabetes, and a weakened immune system. Managing stress can help reduce the risk of these conditions and improve overall health (American College of Lifestyle Medicine).
- Cognitive Function: Reducing stress can improve cognitive functions such as memory, attention, and decision-making. It also lowers the risk of cognitive decline and neurodegenerative diseases.
- Emotional Resilience: Stress management techniques help build emotional resilience, enabling individuals to cope more effectively with life’s challenges and recover from setbacks more quickly.
- Quality of Life: Lowering stress levels can improve overall quality of life, enhancing personal and professional relationships, increasing productivity, and promoting a sense of well-being.
Practical Tips:
- Practice Mindfulness and Meditation: Dedicate time each day to mindfulness or meditation. Apps and online resources can provide guided sessions to help you get started.
- Engage in Regular Physical Activity: Find physical activities you enjoy and make them a regular part of your routine. Even short, daily walks can significantly reduce stress.
- Prioritize Sleep: Follow good sleep hygiene practices to ensure you get adequate, quality sleep. This includes maintaining a consistent sleep schedule and creating a restful sleep environment.
- Maintain Social Connections: Stay connected with friends and family, and seek support when needed. Engaging in social activities can provide a valuable outlet for stress.
- Learn Relaxation Techniques: Incorporate deep breathing exercises, progressive muscle relaxation, or guided imagery into your daily routine to activate the relaxation response.
- Improve Time Management: Set realistic goals, prioritize tasks, and break projects into manageable steps to reduce feelings of being overwhelmed.
5. Avoidance of Risky Substances

Avoiding risky substances focuses on minimizing or eliminating the use of substances that can harm health. These include tobacco, excessive alcohol, and recreational drugs.
Key Aspects of Risky Substances:
- Tobacco:
- Smoking: Cigarette smoking is a leading cause of preventable diseases and death, linked to various cancers, cardiovascular diseases, and respiratory conditions.
- Secondhand Smoke: Exposure to secondhand smoke also poses significant health risks, particularly for children and non-smokers living with smokers.
- Alcohol:
- Moderation: While some studies suggest that moderate alcohol consumption might have certain health benefits, excessive alcohol use is associated with liver disease, certain cancers, cardiovascular problems, and addiction.
- Binge Drinking: Engaging in binge drinking, defined as consuming large amounts of alcohol in a short period, increases the risk of accidents, injuries, and long-term health issues.
- Recreational Drugs:
- Illicit Drugs: The use of illegal drugs can lead to addiction, mental health disorders, infectious diseases (due to needle sharing), and overdose deaths.
- Prescription Drug Abuse: Misusing prescription medications, such as opioids, sedatives, and stimulants, can also lead to addiction and severe health consequences.
- Over-the-Counter (OTC) Medications:
- Misuse and Dependence: OTC medications, while generally safe when used as directed, can be harmful when overused. Regular misuse, especially of pain relievers (e.g., acetaminophen and ibuprofen) and cold medicines containing dextromethorphan, can lead to dependence and serious health complications.
- Liver and Kidney Damage: Excessive use of certain OTC medications, particularly those containing acetaminophen, can cause liver damage, while frequent use of NSAIDs (like ibuprofen) may lead to kidney issues, stomach ulcers, and increased risk of heart problems.
- Masking Symptoms: Overusing OTC medications may mask underlying health conditions, delaying proper diagnosis and treatment, which could worsen the original issue over time.
Benefits:
- Reduced Risk of Chronic Diseases: Avoiding tobacco, excessive alcohol, and recreational drugs significantly lowers the risk of chronic diseases such as cancer, heart disease, liver disease, and respiratory conditions (Thrive50Plus) .
- Improved Mental Health: Substance abuse is closely linked to mental health disorders, including depression and anxiety. Avoiding these substances can improve mental well-being and reduce the risk of developing mental health issues.
- Enhanced Physical Health: Substance avoidance contributes to better overall physical health, improving lung function, liver health, and cardiovascular fitness .
- Better Quality of Life: Avoiding risky substances can enhance the quality of life by improving physical and mental health, increasing life expectancy, and enhancing social and professional relationships.
- Lower Healthcare Costs: Reducing the use of harmful substances can decrease healthcare costs associated with treating substance-related illnesses and injuries.
Practical Tips:
- Seek Support: If you’re struggling to quit smoking, drinking, or drug use, seek support from healthcare professionals, support groups, or counseling services. Programs like Nicotine Replacement Therapy (NRT) for smoking cessation can be effective .
- Educate Yourself: Understand the risks associated with substance use. Knowledge about the health impacts can be a strong motivator for change.
- Healthy Alternatives: Find healthy alternatives to cope with stress and emotions, such as exercise, hobbies, and mindfulness practices.
- Avoid Triggers: Identify and avoid situations, places, or people that trigger cravings for risky substances. Creating a supportive environment can help maintain substance-free living.
- Use Non-Medicinal Approaches When Possible: For mild medical conditions, consider non-drug approaches like hydration, warm baths, or herbal teas before turning to OTC medication. In addition, practice preventive care, such as regular exercise, a balanced diet, and adequate sleep, can also help reduce reliance on OTC medications for minor ailments.
6. Positive Social Connections

Engaging in positive social connections is a key aspect of promoting overall well-being and health. Here are some ways to foster positive social connections:
Key Aspects of Social Connections:
- Build and Maintain Relationships: Cultivate meaningful relationships with family, friends, colleagues, and community members. Invest time and effort in nurturing these connections.
- Communicate Effectively: Practice active listening and open communication. Share your thoughts and feelings honestly, and encourage others to do the same.
- Show Empathy and Support: Be empathetic towards others’ feelings and experiences. Offer support and encouragement when needed, and celebrate their successes.
- Participate in Group Activities: Join clubs, organizations, or teams that align with your interests. Engaging in group activities can help forge new friendships and strengthen existing bonds.
- Volunteer and Give Back: Contribute to your community through volunteering or participating in charitable activities. Helping others can provide a sense of fulfillment and connect you with like-minded individuals.
- Stay Connected: In today’s digital age, maintain connections through social media, video calls, or messaging apps when face-to-face interactions are not possible.
- Set Boundaries: While fostering positive social connections is important, it’s also crucial to set boundaries to protect your emotional well-being. Be mindful of toxic relationships and prioritize those that uplift and support you.
By actively engaging in positive social connections, you can enhance your mental and emotional health, reduce stress, and create a supportive network that contributes to a fulfilling life.
Benefits:
- Emotional Support: Positive social interactions provide emotional support during challenging times and help alleviate feelings of loneliness and isolation.
- Stress Reduction: Strong social connections can reduce levels of stress hormones and buffer the effects of stressful situations.
- Improved Mental Health: Regular social engagement is linked to lower rates of depression and anxiety, promoting better mental health.
- Increased Happiness: Meaningful social relationships contribute to a sense of belonging and fulfillment, leading to greater happiness.
- Physical Health: Studies suggest that strong social connections are associated with better physical health outcomes, including lower blood pressure and reduced risk of chronic diseases.
Practical Tips:
- Be Proactive: Take initiative in reaching out to others and initiating conversations. Invite friends or colleagues for coffee or lunch.
- Listen Actively: Practice active listening by paying attention to what others are saying without interrupting. Show genuine interest in their thoughts and feelings.
- Show Appreciation: Express gratitude and appreciation for the people in your life. A simple thank-you can strengthen relationships and foster positivity.
- Join Clubs or Groups: Participate in clubs, classes, or organizations that align with your interests. This can provide opportunities to meet new people who share similar passions.
- Attend Social Events: Attend social gatherings, parties, or community events where you can mingle and connect with others in a relaxed setting.
- Use Technology Wisely: Utilize social media and online platforms to stay connected with friends and family, but prioritize face-to-face interactions whenever possible.
- Be Supportive: Offer support and encouragement to others in times of need. Show empathy and be there to listen without judgment.
- Set Boundaries: Maintain a healthy balance between socializing and personal time. Respect your own need for solitude and downtime when necessary.
7. Healthy Living Environment

Your living environment plays a surprisingly big role in your overall health and well-being. Just like diet and exercise, the way you design and manage your surroundings can significantly impact your physical and mental health. By focusing on creating and maintaining a healthy living environment, individuals can significantly prevent chronic diseases, and enhance their quality of life.
Key Aspects of a Healthy Living Environment:
- Natural Light and Darkness: Daytime light and total darkness at night can help regulate your circadian rhythm, impacting sleep, mood, and energy levels.
- Air Quality: Poor air quality can lead to respiratory problems, allergies, and fatigue.
- Cleanliness and Organization: Clutter can be visually overwhelming and contribute to stress.
- Safety and Security: A secure living environment promotes safety for the whole family and peace of mind.
- Access to Nature: Spending time in nature reduces stress and improves mood.
- Reducing Toxins: Minimize exposure to harmful chemicals found in cleaning products, pesticides, and building materials. Opt for natural or non-toxic alternatives where possible.
Benefits:
- Sleep Environment: A bedroom that is cool, dark, and quiet promotes better sleep. Good quality mattresses and pillows, along with limiting screen time before bed, are also important.
- Social Connections: Designing spaces that promote social interaction, such as communal gardens or shared recreational areas, can foster a sense of community.
- Stress Reduction: Creating a tranquil and clutter-free living space can help reduce stress. Incorporating elements like plants, artwork, and comfortable furniture can enhance well-being.
- Boosted immune system: Good air quality reduces exposure to pollutants and allergens.
- Increased physical activity levels: Access to nature encourages outdoor activities.
- Enhanced mood and cognitive function: Natural light and reduced stress improve mood and focus.
- Lower risk of chronic diseases: All these factors contribute to a healthier lifestyle.
Practical Tips:
- Maximize Natural Light and Darnkess: Open curtains, consider skylights or light tubes during the day and emphasise natural darkness at night.
- Prioritize Air Quality: Use air-purifying plants or an air purifier, ensure proper ventilation.
- Embrace Cleanliness and Organization: Declutter regularly, establish cleaning routines.
- Feel Safe and Secure: Install proper locks, consider a security system if necessary, and minimize hazardous installations in and around the house.
- Connect with Nature: Houseplants, natural elements, spend time outdoors.




Leave a Reply