It is true when we discuss children playing computer games, the negatives in their indulgence seem to outweigh the positives by miles. Our biased viewpoint is that computer games and other video games are bad news for children!
Well, should you buy into this viewpoint?
Yes, games can be so engrossing and domineering if left unchecked. They can lead to addictive tendencies and neglect of important chores at home and school.
Second, games that subject children to sedentary positions for extended hours are a hindrance to the wellness of their health.
On the bright side, computer games come with a lot of positives when done correctly. They can boost children’s cognitive well-being, in addition to making them creative and innovative.
This is because every computer game ships with varying levels of puzzles and mysteries that have to be solved. There is always a thought-provoking task to be completed before points are earned.
Here are only a few reasons that should give you reasons enough to let your child play
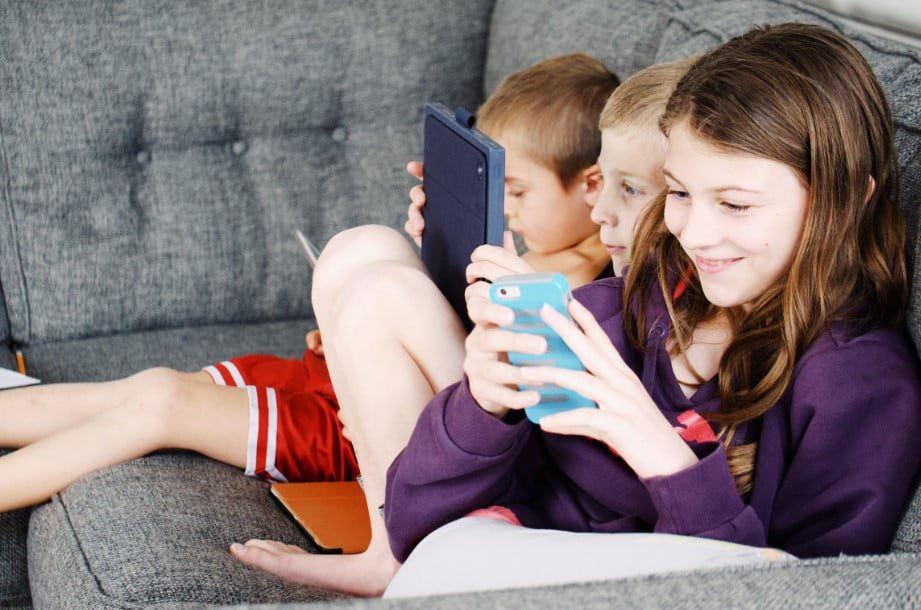

1. Critical thinking & problem solving skills
Playing computer games provides children with opportunities to think far and wide as they seek solutions to the numerous gaming puzzles.
This may involve navigating through cities in search of villains, or figuring out the way back home from dreaded islands. Sometimes, the game involves driving through treacherous terrains and cities.
All these strategies are examples of skills they need to solve real-life challenges and tasks. And unlike other activities in the classroom, games provide real opportunities that require real-time urgency, and therefore prompt solutions.
In the beginning, children will falter in solving these puzzles. They will, however, improve with time and experience. And that is where the learning process starts.
They will up their skills to ensure they don’t arrest the wrong villain or smush the car onto a wall.
They will try out new strategies and tweaks in order not to repeat the same mistakes next time around. For example, they will learn to adjust the breaks in order not to hit the wall and avoid collisions with other vehicles when driving around corners.
Their gaming quests will ultimately make them creative, innovative, confident, persistent, and of course, learn when to quit, instead of wasting time on games they may never conquer.
Sample games to aid in problem-solving skills include:
- Portal
- Turing Test
- Snake Pass
- Talos Principle
2. Visual-spatial skills
Visual-spatial abilities in children describe their abilities to perceive visual objects in space and the environment and being able to manage them intelligently in real life.
It is all about mentally assessing and understanding 2D and 3D constructions of life, based on what they see through the naked eye.
The APA Dictionary of Phycology defines visual-spatial skills as
the ability to comprehend and conceptualize visual representations and spatial relationships in learning and in the performance of tasks such as reading maps, navigating mazes, conceptualizing objects in space from different perspectives, and executing various geometric operations.
In what is known as visual construction, children become better at understanding their presence in the real environment, thereby wading their way through distractions and obstacles with measured intelligence.
Numerous studies have shown that kids who play computer games develop better visual-spatial competencies.
This is especially true in games where they are represented by characters on the screen, and where they learn to appreciate their presence in relation to other objects and distractions.
Eventually, they pay visible attention to details in real-life environments and people around them. They are more likely to notice and conceptualize objects such as trees, plants, architectural designs, mathematics, and physics, in greater detail.
They are also more likely to drive well and find their way in a new city with ease.
Just as well, pro-social games can instill in them the willingness to help others in real life.
Sample computer games that aid visual-spatial skills include:
3. Eye-hand coordination
Eye-hand coordination, also known as visuomotor control defines the ability to coordinate the movements of the eye and hand while accomplishing everyday tasks.
This motor skill is crucial in real life and is reflected in quick thinking and precise reactions to fast-moving tasks.
Eye-hand coordination is reflected in action and sporting games when children use their eyes and hands to play and drive with accuracy and speed. The simultaneous ability to coordinate the eye and hand movements on the joystick and other gamepads, allows them to excel or fail in the game.
Their efficiency is then reflected in sports such as basketball, soccer, and athletics.
A study in 2016 by Li Li, Rongrong Chen, and Jing Chen concluded that PC games foster eye-hand coordination, and improve the effective use of hand and eye coordination in real life.
action gamers have better lane-keeping and visuomotor-control skills than do non–action gamers.
Psychological Science
In real life, therefore, gamers perform better in sensorimotor activities such as soccer, riding, driving, and other actionable activities.
Sample computer games that aid eye-hand coordination:
- FIFA
- World of Warcraft
- Topspin
- Traffic Rush
4. Language development
When children are playing computer games they want to be fully involved and partake in the conversations taking place in their favorite games.
Knowingly or unknowingly, they use a set of 3 or even 4 language skills in order to excel in their adventures. These include listening, speaking, and reading, and yes writing in some games.
And far away from the classroom environment where acquisition of these skills is labored, games provide an alternative yet exciting and subconscious effort in learning a first or even a second language.
By playing games, children learn to
- listen to instructions and other players
- speak to opponents and peers
- read instructions on the screen
- write words and expressions in games such as Scribblish and Scrabble
Essentially learning through games is much more contextual and similar to learning in a new environment.
Even better, because kids play the same games repetitively they quickly relearn words and expressions and easily apply them in context.
Yes, learning language skills may sound erratic and not necessarily pro grammar, still, computer games promote the acquisition of new sets of vocabulary and creative use of sentences.
This is supported by a study by Gothenburg and Karlstad Universities in Sweden which showed that individuals who played computer games regularly amassed a large vocabulary, particularly in the English language.
Sample video games to boost language development:
- Telltale
- Game of Throne
- Skyrim
- Crossword puzzle
5. Collaboration skills
Most computer games are based on group play, and can foster how children relate with other people. Multiplayer games that pair children teaches them to work together to solve mutual gaming challenges.
Games which give players options to occupy virtual rooms deepen the collaboration skill, because children find they have to stay together in virtual spaces and support each other.
Through collaboration, children learn to work as a team, make compromises, be flexible, and win or lose together.
The popular Minecraft game is built on a background of creativity and allows children to work together, to tap on each others imagination.
6. Executive functioning skills
Numerous studies continue to suggest how computer games can foster the development of executive functions skills. These are higher-level mental skills often categorized under three headings:
According to Science Direct,
… active video game play may have positive effects on some executive functions with implications for real-world behavior.
By playing select computer games children can excel in real-life tasks such as planning, organizing, focusing, managing time, and enhancing their flexibility in thought and managing emotions.
Children are not necessarily born with executive functions, but learn them through support from parents and other members of the community. These persons set up scaffoldings and other structures that enhance the learning of the skills.
Where parents are not supportive enough as is the case in the 21st century, children learn these lifelong skills on their own – or not at all. One option parents can use to foster these skills is through select computer games.
Sample games to boost the executive functions:
- Hallo
- Scrabble
- SimCity
- StarCraft
In conclusion
Once again, computer games have their positives and negatives. To ensure the positives win the day, gaming should be done selectively and in moderation. Preference should be given to adventures, safe-action, and pro-social games instead of extremely violent games! This is particularly true for the very young ones.




Leave a Reply